Headings
Headings and subheadings should be identified using the built-in features of the program you are using to create your document. Manual bolding and enlarging of text won't be detected as a heading by screen readers.
In Word 2016, heading styles are available on the Home ribbon.
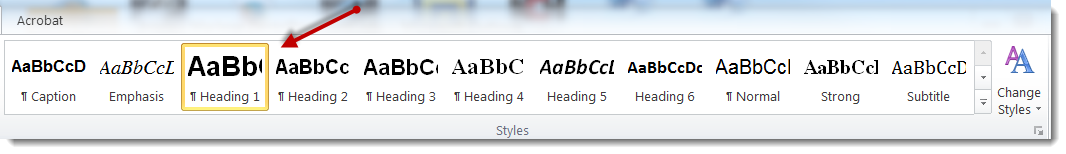
Headings should have a meaningful hierarchy and should be used sequentially.
- Heading 1
- Heading 2
- Heading 3
- Heading 3
- Heading 2
- Heading 3
- Heading 4
- Heading 4
- Heading 3
- Heading 3
- Heading 2
- Heading 2
Headings form an outline of the content. For example, the document title would be Heading 1, individual sections would be Heading 2, subsections would be Heading 3, etc. This enables users to understand how the page is organized, and to quickly navigate to content of interest.
Tips
-
You can change the appearance of headings by right-clicking a particular heading style (example: Heading 1) and selecting "Modify Style."
-
When your headings are formatted properly, you can easily create a dynamic table of contents in the References tab.
-
A document map can help you navigate through the document while editing. View the document map by enabling "Navigation Pane" in the View tab.
