Simulation Parameters
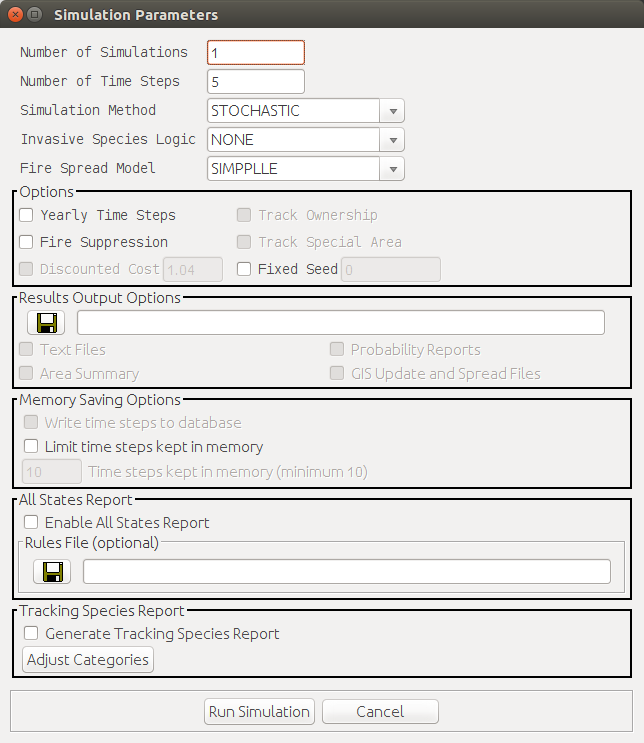
Simulation Options
Number of Simulations
The number of simulations to run depends on both the size and the variability of vegetation within the area. Based on previous work, 30 simulations appear to be adequate to capture the variability created within OpenSIMPPLLE. An Excel spreadsheet with a statistical test is provided to make it possible to test sets of simulations to see if additional simulations increase the variability of specific attributes.
Single simulations are often used to check system behavior and to gain an understanding of how changes have an interacting effect on many processes. The short time it takes to make an OpenSIMPPLLE simulation makes it easy to use in a team environment to test system knowledge.
Multiple simulations are most often used to help quantify a range of outcomes on management options once they have been designed. A statistical test is provided with the Microsoft Excel spreadsheet template that comes with OpenSIMPPLLE to compare the distribution of outcomes to see if there are any significant differences. Multiple simulations can be used to provide quantification for the concept of a range of variability in both vegetation attributes and disturbance processes. They can be used with long-term simulations to help provide a quantification of historic landscape conditions. When making multiple simulations, you have the option of tracking by ownership and special area within the data set. This enables the file using the Excel macro to be stratified by these levels. When making multiple simulations, a location and a prefix go with the files that are created must be specified.
Number of Time Steps
Short-term simulations (1-5 decades) are often used to provide a means to compare alternative management scenarios or current trends.
Long-term simulations (greater than 5 decades) are most often used to help quantify the interaction and cycling of disturbance processes and vegetation conditions. Long-term simulations lasting 5-10 decades without fire suppression are one way to help provide a quantification of historic conditions for a specific landscape.
Simulation Method
Stochastic is the most common simulation method used. A Monte Carlo approach is used with the probability values for each disturbance process calculated for each individual plant community to reinforce the concept that our landscapes are not always shaped by processes that have a high probability of happening on any given acre. The probability of many events is relatively low, but when these disturbance events happen, they make significant changes that shape the development of the landscapes. Stochastic, multiple simulations can be used to create the probability of vegetation attributes existing or disturbances occurring within a landscape. They are also useful to help add quantification to the concept that there is variability in the outcome in our landscapes. For some analyses on a very specific location of treatment choice, for example fuel management treatments, it may be more useful to lock-in specific disturbance processes to see how the landscape will vary with or without the treatments.
Highest Probability will utilize the disturbance process that has the highest probability for each plant community.
Stand Development eliminates all disturbance processes. This will create a landscape in which all plant communities simply grow older.
Invasive Species Logic
This can be used only if the logic is included for the geographic zone or area in use. These areas are the Colorado Plateau and the east side of Region One.
Fire Spread Model
SIMPPLLE
KEANE
Yearly Time Steps
The default time step is a decade. However, some of the interactions between processes, such as fire, insects, or the response of grasses to yearly moisture changes, make more sense if the system is run with yearly time steps. For some geographic areas, such as the grasslands, the interaction between processes is important on a seasonal basis. For these geographic areas, the default time step is yearly. For geographic areas where the user can choose between yearly or decade time steps, most system knowledge is automatically adjusted. Two system knowledge components that the user must adjust are:
- Regeneration delay
- Rate of change for tracking species when used for invasives
Both of these changes can be made through the user interface.
Fire Suppression
Simulations to compare management options are usually made with fire suppression. Making simulations without fire suppression is most commonly used with long-term simulations to create an interaction between fire, insect, and disease disturbances and the vegetation pattern to quantify a historic range of variability. If fire suppression costs are incorporated, however, they are very simplistic. Fire suppression costs can be edited through the dialog in System Knowledge > Vegetative Process > Fire Suppression Costs. Costs are assigned on a per-acre basis, by fire size class, and by fire management zone.
Discounted Cost
Discounted cost calculates and discounts the fire suppression costs at the rate specified. This option is unavailable until fire suppression is enabled.
Track Ownership
If ownership is attributed in the landscape file, then the option to have an output file stratified by these levels can be enabled. This can only be selected for multiple simulations.
Track Special Area
If special area is attributed in the landscape file, then the option to have an output file stratified by these levels can be enabled. This can only be selected for multiple simulations.
Fixed Seed
...
Output Options
Text Files
...
Area Summary
...
Probability Reports
...
GIS Update and Spread Files
...
Memory Saving Options
Write Time Steps to Database
...
Limit Time Steps Kept in Memory
Reduces memory requirements by limiting the number of time steps kept in memory during a simulation. There is a minimum number of time steps to keep in memory, since some of the logic associated with disturbance probabilities references prior disturbance and treatment history. The default and minimum are set to 10 time steps. The Eastside Region One zone requires a minimum of 20 time steps for logic associated with the confifer encroachment process.
All States Report
Enable All States Report
...
Tracking Species Report
Generate Tracking Species Report
...
Adjust Categories
...
